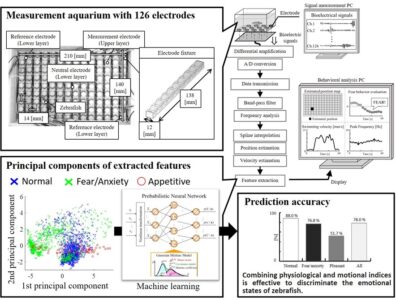
Using 126 electrodes placed on the bottom of an aquarium, we measured the bioelectrical signals of zebrafish (Danio rerio), which are about 3 cm long. By extracting respiratory and motor information from the bioelectrical signals and discriminating them using a neural network, we have succeeded in estimating the emotional states of the fish, such as fear/anxiety and pleasure states.
Research topics
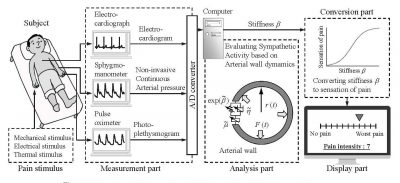
Peripheral Arterial Stiffness Positively Correlates with Pain-Related Brain Activity
Medical engineering groupWe measured brain activity, peripheral arterial stiffness as an index of peripheral sympathetic nerve activity, and subjective evaluation using visual analogue scales (VASs) when painful stimuli were applied to the skin surface of the participants. Experimental results clarified that the brain activities in some pain-related brain areas were significantly correlated with the peripheral arterial stiffness.

Objective Pain Evaluation
Medical engineering groupWe analyzed the relationships among changes in vascular dynamics characteristics governed by sympathetic nerve activity, skin electrical stimulation accompanied with pain, and subjective pain intensity. As results, certain relationships were found among them.
Sphygmomanometer using Electromagnetic Induction
Medical engineering groupWe proposed a novel sphygmomanometer that enable an evaluator to palpate the carotid artery wave of the subject. Specifically, the proposed sphygmomanometer has the following advantages: (1) continuous arterial pressure with a high SN ratio can be measured by the proposed sensor; (2) the evaluator can perceive the carotid artery pressure through the sphygmomanometer; and (3) The sphygmomanometer is compact and easy to detach.
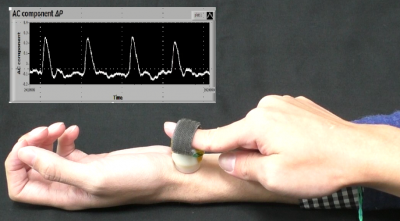
Evaluating a Vascular Endothelial Function
Medical engineering groupEnclosed zone flow-mediated vasodilation (ezFMD) is a vascular endothelial function evaluation method using the oscillometric method. We proposed a novel endothelial function evaluation index considering the mechanical measurement principle of ezFMD, and validated its effectiveness.

Log-linearized Peripheral Arterial Viscoelastic Model
Medical engineering groupIn this study, we proposed a log-linearized peripheral vascular viscoelastic index by deriving an approximate model of vascular dynamics that considers the intravascular pressure in the peripheral vasculature and the nonlinear characteristics of the vascular system.
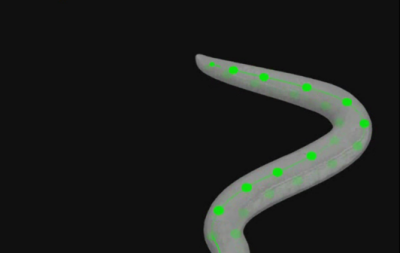
Neural Network Model of Caenorhabditis elegans and Simulation of Chemotaxis-related Information Processing in the Neural Network
Kansei brain groupThis study proposed a neural network model of Caenorhabditis elegans, for which the connectome has been elucidated. The connectome-based neural network model enables the simulation of chemotaxis, and is thus expected to contribute to the design of guidelines for actual biological experiments that aim to determine the information processing mechanism of chemotaxis.
Bioassay System Based on Behavioral Analysis and Bioelectric Ventilatory Signals of a Small Fish
Kansei brain groupThis study focused on the bioelectric (ventilatory) signals of small fish and proposed a bioassay system for detecting water pollution by simultaneously monitoring fish behavior and ventilatory signals.

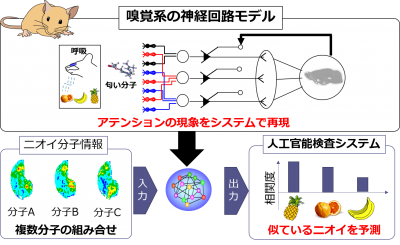
Mathematical Model of the Olfactory Bulb for the Selective Adaptation Mechanism in the Rodent Olfactory System
Kansei brain groupTo predict the perceptual similarities of odor pairs from neural activities of the olfactory system, we proposed a neural net model based on the olfactory system structure.
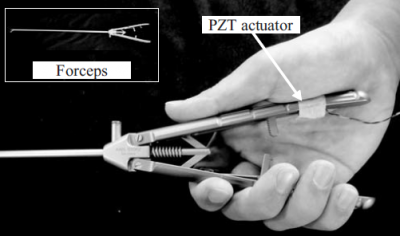
Surgical Grasping Forceps with Enhanced Sensorimotor Capability via the Stochastic Resonance Effect
Human modeling groupA phenomenon known as stochastic resonance (SR) improves the perceivable threshold based on the application of weak vibration to receptors. We proposed the concept of surgical grasping forceps with enhanced sensorimotor capability by attaching a vibrator to the forceps’ grip and evoking the SR effect.
Stiffness display by muscle contraction via electric muscle stimulation
Human modeling groupWe developed a haptic force display system that renders different levels of stiffness using electrical muscle stimulation (EMS). We analyzed the performance of our system by measuring the perceived stiffness in human experiments. The experimental results show a positive correlation between the target stiffness and perceived stiffness.
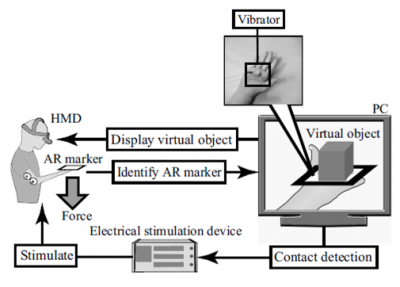
Unpowered sensorimotor-enhancing suit reduces muscle activation and improves force perception
Human modeling groupThe purpose of this study was to develop a sensorimotor-enhancing suit (SEnS)—unpowered assistive clothing without actuators or electrical devices—and examine its efficacy for reducing voluntary muscle activation and improving force reproduction in the upper limbs of healthy young adults.

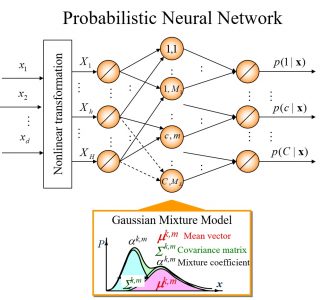
Novel Probabilistic Neural Network
Bioelectric signal groupWe proposed a novel neural network based on stochastic/statistical theory, and applied it to the development of learning control technology in robots and medical welfare equipment and for the classification of medical data.
A Clinical Diagnosis Support System for General Movements Evaluation to Assess Spontaneous Movements in Infants
Bioelectric signal groupIn this study, we proposed a markerless infant movement assessment system to evaluate general movements (GMs) in infants using video images.

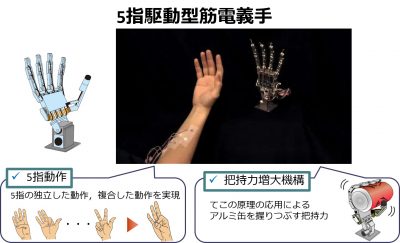
Electromyographic Prosthetic Hand using Grasping-Force-Magnification Mechanism with Five Independently Driven Fingers
Bioelectric signal groupWe developed an electromyogram (EMG) prosthetic hand that has five independently driven fingers. The hand includes a flexion drive and a force-magnification drive, allowing rapid finger motion and a firm grasp.
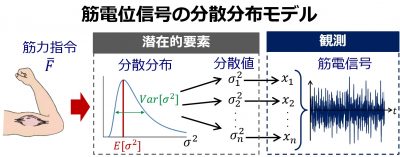
Variance Distribution Model of Surface EMG Signals Based on Inverse Gamma Distribution
Bioelectric signal groupIn this study, a novel stochastic model for surface electromyogram (EMG) signals was proposed. In the model, the variance of EMG signals is handled as a random variable, thereby allowing the estimation of signal-dependent noise that cannot be represented in previous EMG models.